Anti-inflammatory Diet – Food to decrease inflammation and enhance overall health
An anti-inflammatory diet contains food that helps to decrease chronic hives in the body, which are associated with different health requirements such as diabetes, arthritis, heart diseases, and even cancer. Chronic inflammation happens when the immune system stays constantly activated, usually due to harmful dietary choices, environmental impacts, or stress, and can lead to ongoing health issues. An anti-inflammatory diet helps to handle this by including foods that restore balance, boost the immune system, and lower inflammation.
Components of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
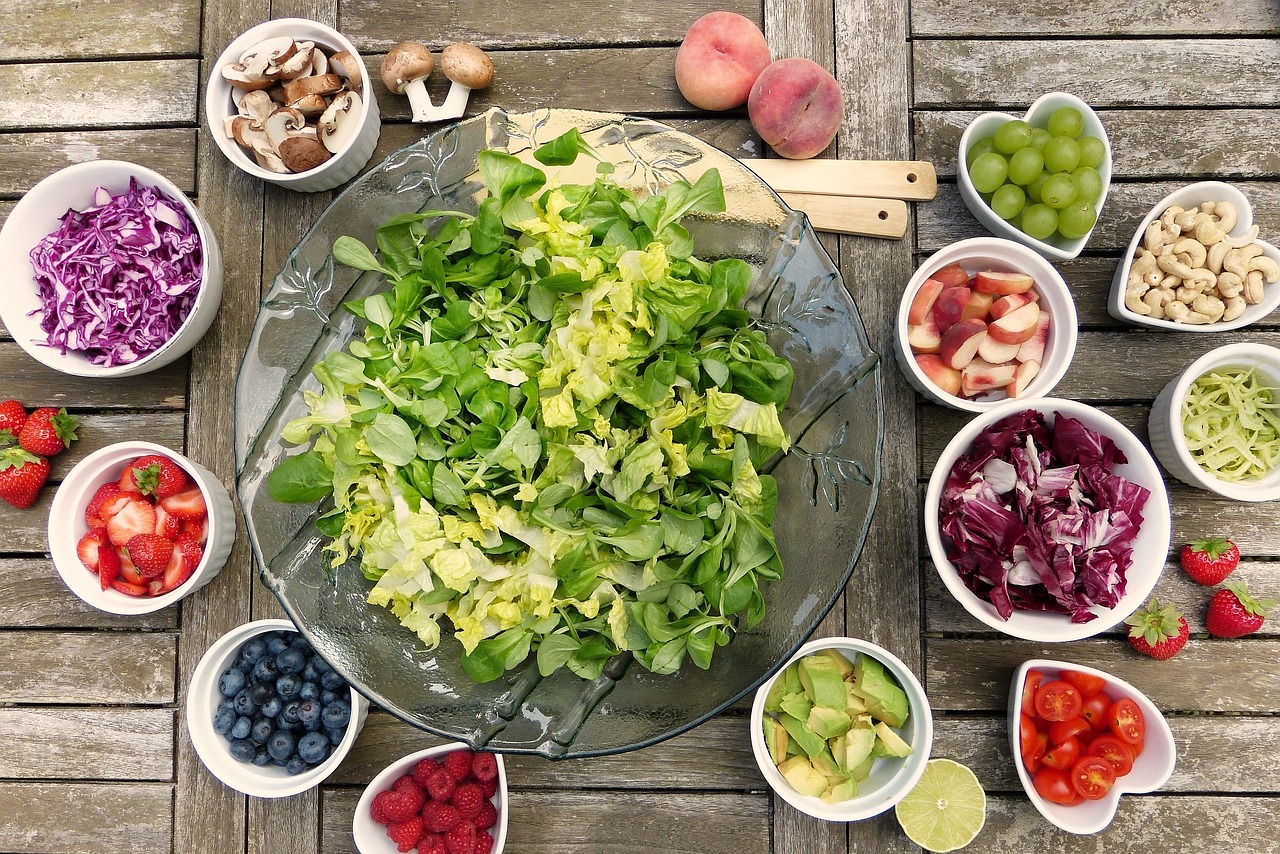
1. Vegetables and Fruits:
Tomato is a powerful antioxidant that decreases inflammation and rich origin of lycopene.
Leafy green vegetables help to regulate inflammatory paths and are rich in seeds of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Cruciferous vegetables such as cauliflower, broccoli, and Brussels outgrowths contain anti-inflammatory belongings.
To fight hives, berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and jeers are rich sources of antioxidants like flavonoids.
2. Seeds and Nuts
- Seeds such as flaxseeds and chia seeds are a good source of fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Nuts including almonds, pistachios, and walnuts are high sources of fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants that are helpful in the reduction of inflammation.
3. Spices and Herbs
- Turmeric containing curcumin is a high source of anti-inflammatory factors.
- Ginger and Garlic are also natural sources of reducing anti-inflammation.
- Cinnamon is also common for its anti-inflammatory properties and also helpful in regulating blood sugar.
4. Green Tea
Green tea is a rich source of polyphenols that contain compounds that help support cellular health and reduce inflammation.
5. Whole grains
Whole grains are a high source of fiber which supports blood sugars, and digestive health and also helps in reducing inflammation.
6. Probiotic-Rich Foods
Foods that are rich in probiotics promote a healthy gut microbiome and reduce inflammation.
7. Water and Hydrating Beverages
Water and other hydrating beverages help stay hydrated, remove toxins, and reduce inflammation.
8. Lean Proteins
Plant-based and lean animal proteins are less inflammatory than processed red meats.
9. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, olive oil, avocado, and nuts are rich sources of fats.
Foods Need to be Avoided in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet has many health benefits by promoting foods that reduce inflammation and support overall health. Here are some advantages:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Chronic inflammation is linked to diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. An anti-inflammatory diet can lower the risk of these problems by reducing inflammation.
Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber can improve cholesterol levels which helps to reduce blood pressure, support heart health, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Whole grains, probiotic foods, and fiber-rich fruits in an anti-inflammatory diet promote a healthy gut microbiome and digestion, which are essential for better immune function and overall health.
Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats help to reduce skin inflammation and protect skin cells, which contribute to a fair complexion and a reduction in skin problems like acne and eczema.
- Increased Energy and Mental Clarity Consuming whole foods, balanced meals, and healthy fats provides steady energy levels throughout the day which helps in avoiding the crashes associated with processed foods and sugars. This can also lead to improved focus and mental clarity.
- Weight Management and Metabolic Health
An anti-inflammatory diet emphasizes whole foods that are filling and nutrient-dense, which can help in weight management, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce blood sugar spikes, supporting metabolic health.
By taking nutrient-rich foods and reducing inflammatory triggers, an anti-inflammatory diet can support a healthier, balanced lifestyle and help to manage or prevent various health problems.
Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet:
In an anti-inflammatory diet, inflammation can be reduced by avoiding certain foods and by doing this, overall health will become better. These are the foods to avoid:
1) Fried and Processed Foods
This includes fast food, potato chips, french fries, deep-fried items such as chicken, fish, doughnuts, and other heavily processed snacks. These foods contain unhealthy oils and trans fats that promote inflammation which leads to heart disease.
2) Red and Processed Meats
These products include beef, pork, lamb, sausages, hot dogs, bacon, and deli meats. Processed meats contain added preservatives and nitrates while red meats contain saturated fats, both are linked to increased inflammation and a higher risk of chronic diseases.
3) Excessive Alcohol
Alcoholic beverages, especially in high amounts can lead to inflammation. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits, excessive intake promotes inflammation and has a negative impact on immune function and liver health.
4) Refined Carbohydrates and Sugary Foods
White bread, pastries, sugary cereals, white rice, soda, cookies, candy, and other sweetened beverages can cause blood sugar spikes, increasing the risk of conditions like diabetes and obesity and leading to inflammation.
5) High-fructose corn Syrup and Artificial Sweeteners
Sweetened beverages, many processed snacks, and certain low-calorie or "sugar-free" products also cause inflammation. High-fructose corn syrup has been linked to inflammation and metabolic issues, while some artificial sweeteners may trigger inflammation and disrupt the gut microbiome.
6) Processed Vegetable and Seed Oils
Soybean oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, and other refined vegetable oils are used in many processed foods. These oils are high in omega-6 fatty acids, which can lead to an imbalance with omega-3s, when consumed in excess, leading to inflammation.
7) Excess Salt and Sodium-Laden Foods
Processed snacks, instant noodles, canned soups, frozen meals, and condiments contain excess salt. Intake of high sodium can cause water retention and may contribute to inflammation, especially in individuals sensitive to salt or patients with high blood pressure.
By reducing or avoiding these foods, an anti-inflammatory diet lowers the risk of chronic inflammation, supports the body’s natural balance, and promotes good health.
In summary, an anti-inflammatory diet is an effective way to support long-term health and lower the risk of chronic diseases. Centered around whole, nutrient-rich foods that naturally reduce inflammation—such as fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, whole grains, and lean proteins—this diet helps regulate the body’s immune response and enhances overall wellness.
Additionally, avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and inflammatory ingredients like trans fats and excess sodium helps the body function at its best and lowers the risk of chronic inflammation. Ultimately, an anti-inflammatory diet is more than just reducing inflammation; it’s a sustainable eating approach that boosts energy, enhances mental clarity, and safeguards against numerous health conditions, benefiting both body and mind.